| RETURN | Digital Signaling |
DS-1 Foreign Exchange Signaling
Described in the following subsections are the signaling states used within Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) and Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) modules. This signaling supports 2-Wire FX (Foreign Exchange) Trunk and OPX (Off-Premise Extensions) applications.
Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) modules provide analog circuit INTERCONNECTION TO A CENTRAL OFFICE.
Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) modules provide analog circuit INTERCONNECTION TO A STATION (TELEPHONE OR PBX FX TRUNK).
These signaling methods require 4-state signaling, so both the A and B-Bits are used to represent these signaling states. (In the case of ESF, the C-Bit follows the state of the A-Bit and the D-Bit follows the state of the B-Bit).
Ground Start
This mode of operation is most commonly used in Foreign Exchange (FX) trunk applications.
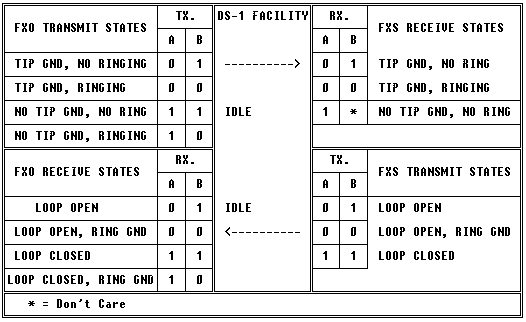
Note: The FXO module will not normally transmit the A=1, B=0 (No Tip Ground,
Ringing), since this state does not exist in the normal Ground Start
environment.
If a FXO channel's TIP AND RING LEADS ARE REVERSED, the Idle State
(A=1, B=1) is correct. But, when an incoming Ground Start call is
placed to the FXO module, THE TIP/RING REVERSAL CAN BE DETECTED IF,
DURING RINGING, THE A-BIT = 1 AND THE B-BIT TOGGLES AT A RATE OF 4
SECONDS OFF (B = 1) AND 2 SECONDS ON (B = 0).
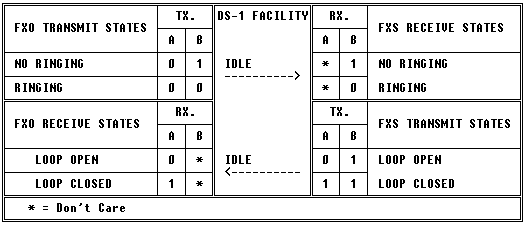
Loop Start
This mode of operation is most commonly used in OPX (Off-Premise Extension) applications. This is a 2-State signaling scheme, using the “B-bit” for signaling.