| RETURN | Home |
Transmission Systems
This document presents information on telecommunications transmission systems.
- Radio Communications
- Cable Communications
Radio wave transmission was traditionally the cornerstone of long-haul communications in the United States. It has been replaced by Fiber Optic cable, which offers greater data rates.
As a general rule of thumb, the higher the RF frequency, the greater the amount of bandwidth that can be carried. Therefore, the GHz bands offer the greatest “bang for the buck”. Unfortunately, the GHz bands are:
- shared with satellite and terrestial microwave frequencies.
- directional (e.g. “line-of-sight”).
- are affected by atmospheric conditions (rain and moisture) and oxygen absorption.
| RF Transmission | Click here for more information on Radio and RF Transmission |
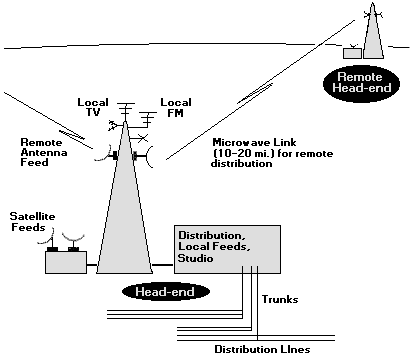
Line Of Site (LOS) Microwave radios are frequently deployed in Community Antenna TV (CATV) systems:

Cable Transmission
There are two types of cable transmission systems:
- Broadband
- Baseband
BroadbandThe term “Broadband” originated in the Cable TV industry. Broadband transmission involves the transmission of multiple channels over a cable system using RF-based modulation principles (Frequency Division Multiplexing).
- Cable Television
- DMT-Based DSL Services
Baseband
The term “Baseband” is used to indicate a single channel, digital transmission over the cable facility.
- Ethernet
- DSL Services
- Basic Rate ISDN (BRI)